In order to create your own 2D derivation views, you have the following elements to use:
Template: Definition of a unique identifier
Description: Definition of the display name
Grid: A grid structure for placing several elements.
Box: A placeholder element to determine position and degree
Derivation: A single 2D derivation view
Text: Positionable and scalable text with deposited translations
Table: Positionable and scalable BOM-list
Should several single elements be combined, the element Frame is used. This is then the parent element for all elements placed on top of it.
The element Formats determines, whether and which Paper formats are available for a certain view.
Under
$CADENAS_SETUP/layouts/2dderivation, create your own dw file by copy and modify it.Under "name", assign a unique name.
[Template] name=drawing_3_views_eu_test1 unitbase=mm translation=dwtext.def [Description] default=Test 1 german=Test 1 [ELEMENT_grid1] type=grid padding_x=10 padding_y=10 padding_unit=percent columns=2 rows=2 order=none,top,front,left
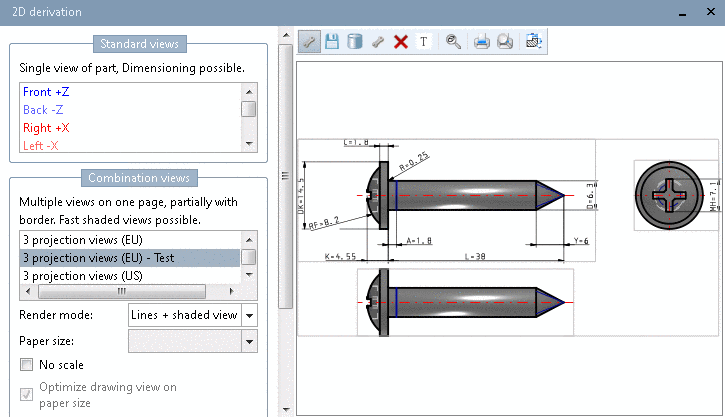
Select a part and in the toolbar click on the 2D derivation button.
-> The own view is now added to the list.
![[Note]](https://webapi.partcommunity.com/service/help/latest/pages/cn/ecatalogsolutions/doc/images/note.png) | Note |
|---|---|
Concept for use of frames and different paper formats: Via [ELEMENT_frame] in the template file *.dw a default frame can be defined. If views for different paper formats are to be created, a separate configuration file is defined for each format via [Formats]. The configuration file in turn references to a specific dxf file (paper format) under [ELEMENT_frame]. | |
![[Note]](https://webapi.partcommunity.com/service/help/latest/pages/cn/ecatalogsolutions/doc/images/note.png) | Note |
|---|---|
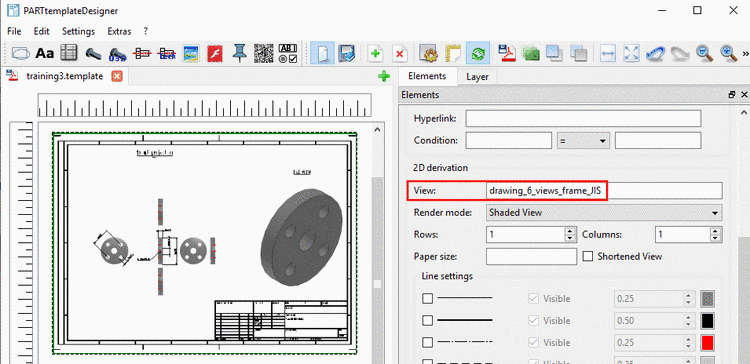
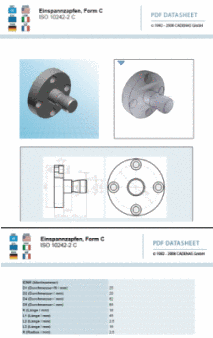
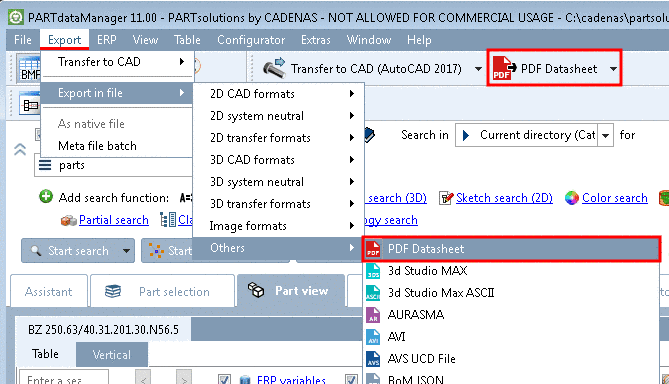
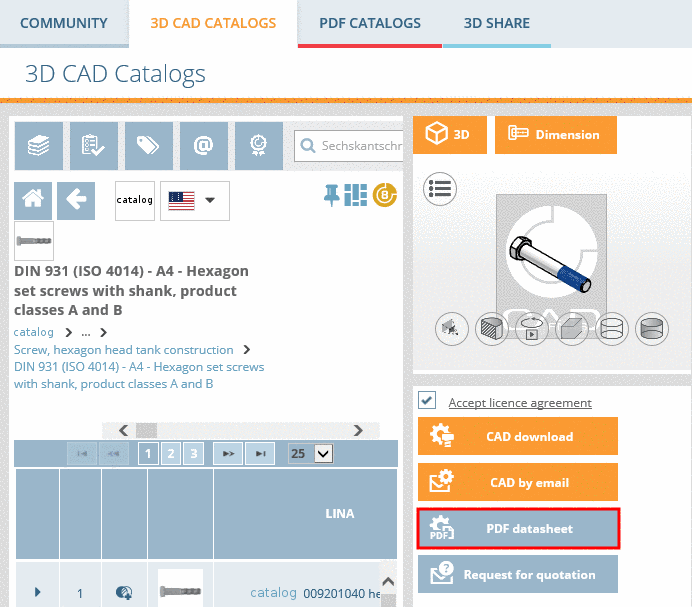
2D derivations (dw files) can directly be used in the PARTtemplateDesigner for the 3D PDF data sheet function, which is provided on the platforms PARTcommunity, PARTserver, PARTsolutions and Offline CDs. See Chapter 10, PARTtemplateDesigner - Create datasheets .
| |